|
Sex-Linked Inheritance: Drosophila
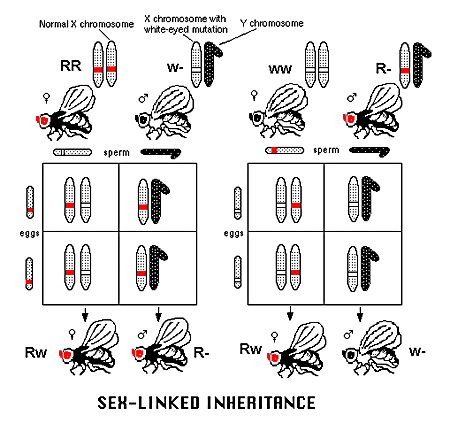
Legend:
Drosophila are used to illustrate how alleles on sex chromosomes are inherited in predictable patterns.
In sex-linked inheritance, alleles on sex chromosomes are inherited in predictable patterns.
For example, in Drosophila the locus for eye color is located on the X chromosome.
The allele for red eye color, which is normal in wild flies, is dominant to the mutant allele for white eyes.
As females have two chromosomes X (with a locus for eye color), they might be homozygous or heterozygous for either allele.
Males, who carry only one X chromosome, are always hemizygous. They carry only the one X chromosome inherited from their mother, and it determines their eye color.
In the left hand example, homozygous red eyed females (RR) mate with hemizygous white eyed males (w-). In the offspring, all the daughters are red eyed heterozygotes (Rw) and all sons are red eyed hemizygotes (R-).
In the right hand, homozygous white eyed females (ww) mate with hemizygous red eyed males (R-).
In the offspring, all the daughters are red eyed heterozygotes (Rw) and all sons are white eyed hemizygotes (w-). | 


