 Mendel: Experiment 1 Mendel: Experiment 1
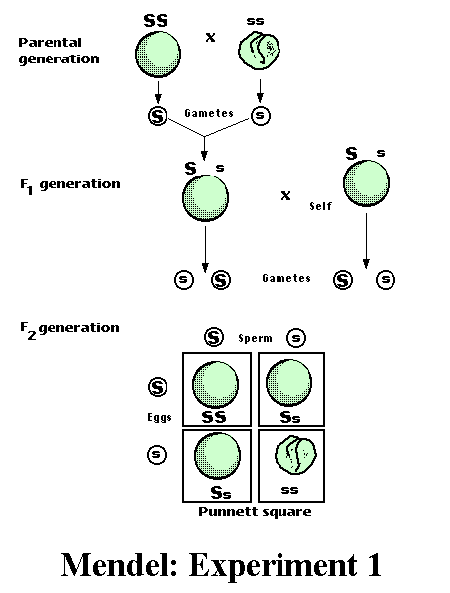
Legend:
This drawing illustrates Mendel's "Experiment 1", in which he
demonstrated his concept of heredity in the mating of pea plants.
Mendel suspected that heredity depended on contributions from both parents
and that specific characteristics from each parent were passed on, rather
than being blended together in the offspring.
A parent homozygous for
the spherical seed allele is crossed with a parent homozygous for the
wrinkled seed allele. Each parent makes gametes of only one kind, either S
or s, and these combine at fertilization to form plants that all have
the genotype Ss and the spherical seed phenotype.
When the F1 plants
self-pollinate they produce two kinds of eggs, S and s, and the same two
types of male sex cells. These combine randomly in four different ways to
form F2 plants.
Three of the four possible combinations produce "spherical seed"
phenotype, and the fourth produces "wrinkled seed" phenotype, so
that the observed ratio is 3:1.
The wrinkled seed phenotypes can only correspond to the "ss"
genotype. The spherical seed phenotype corresponds, in one case to the "SS"
genotype, and in the two others to the "Ss" genotype. Two of
the offsprings are homozygous (SS or ss), the two others
are heterozygous (Ss).
The fact that the
spherical seed phenotype is observed with the genotypes "SS"
or "Ss" can only be explained if the character
"spherical seed" is dominant and the character "wrinkled seed" recessive.
The illustration at the
bottom of the page, called a Punnett Square, is a handy device for keeping
track of the different ways in which gametes combine at fertilization. | 
